DevelopersDocumentation
Keon WiFi SDK Guide
Step-by-step guide to connect your Keon WiFi device with a client app (mobile, web or desktop) using the Keon WiFi SDK for React.
Before You Begin
- Get your partner key: Follow the instructions
at Control Plane API Docs to
obtain your
<partner-key>. - Exchange for a partner token: Use your
<partner-key>to request a<partner-token>, which must include auser-id. - Make sure you have added the SDK to your project:
npm install @feelrobotics/keon-wifi-sdk-react
# or
yarn add @feelrobotics/keon-wifi-sdk-react
Additionally, you can find a sample application in our public repository: GitHub
SDK Method Descriptions
getTokenForKeonWiFi
Function Signature:
async getTokenForKeonWiFi(feelAppsToken: string, deviceConnectionKey: string): Promise<[string, string]>
Description: Authenticates with the Feel Technology server infrastructure to obtain the necessary tokens for device
provisioning. This function takes a Feel Apps token (aka partner-token) and an optional device connection key, then
communicates with the server to retrieve a registration token. The registration token is required for provisioning WiFi
credentials to Keon devices, while the device connection key is used for subsequent server communications.
Returns: A promise that resolves to a tuple containing (registrationToken, deviceConnectionKey). Both values can be null if authentication fails.
provisioningKeonWiFi
Function Signature:
async provisioningKeonWiFi(registrationToken: string, ssid: string, password: string): Promise<[Keon, any]>
Description: Performs the complete WiFi provisioning workflow for a Keon device. This function automatically handles the entire Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connection process, including device discovery, connection establishment, WiFi credential transmission, and disconnection. It creates a new Keon instance, connects to the device via BLE, sends the WiFi network credentials along with the registration token, and then cleanly disconnects from the device. Returns: A promise that resolves to a tuple containing (keonDevice, deviceData) where keonDevice is the Keon instance used for the connection and deviceData contains information about the connected device.
deviceData = {
"device.id": "W5NDAdehXec9lcccYvum6Q==",
"device.name": "KEON WIFI",
"Firmware Version": "V3.0.0b",
"Manufacturer Name": "",
"Serial Number": ""
}
keonWiFiManager
Function Signature:
async keonWiFiManager(feelAppsToken: string, registrationToken: string, userActionHandler: (message: any) => void): Promise<KeonManager>
Description: Creates and initializes a KeonManager instance for ongoing communication with a provisioned Keon device over WiFi. This function establishes a WebSocket connection to the Feel Technology server infrastructure using the provided tokens, enabling real-time bidirectional communication with the device. The user action handler callback function is invoked whenever messages are received from the device, allowing the application to respond to device events and status updates.
Returns: A promise that resolves to a configured KeonManager instance ready for device communication.
KeonManager
Class Description: A comprehensive management class that handles persistent communication with Keon WiFi devices through the Feel Technology server infrastructure. This class provides methods for sending commands to devices, receiving status updates, managing connection state, and handling real-time device interactions. It maintains Socket.io connections to the server and provides a high-level interface for device control and monitoring.
Key Features:
- Real-time bidirectional communication with devices
- Connection state management and automatic reconnection
- Device status monitoring and reporting
- Command queuing and response handling
- Event-driven architecture with user-defined callbacks
Usage: Typically instantiated through the keonWiFiManager function rather than directly constructed, as it requires
proper server credentials and connection setup.
These methods work together to provide a complete workflow: authenticate with servers (getTokenForKeonWiFi), provision devices with WiFi credentials (provisioningKeonWiFi), and maintain ongoing communication (keonWiFiManager + KeonManager).
Interaction Lifecycle
The workflow has two main stages:
- Provisioning the Keon WiFi device
- Sending and receiving commands and status updates
1. Provisioning the Keon WiFi Device
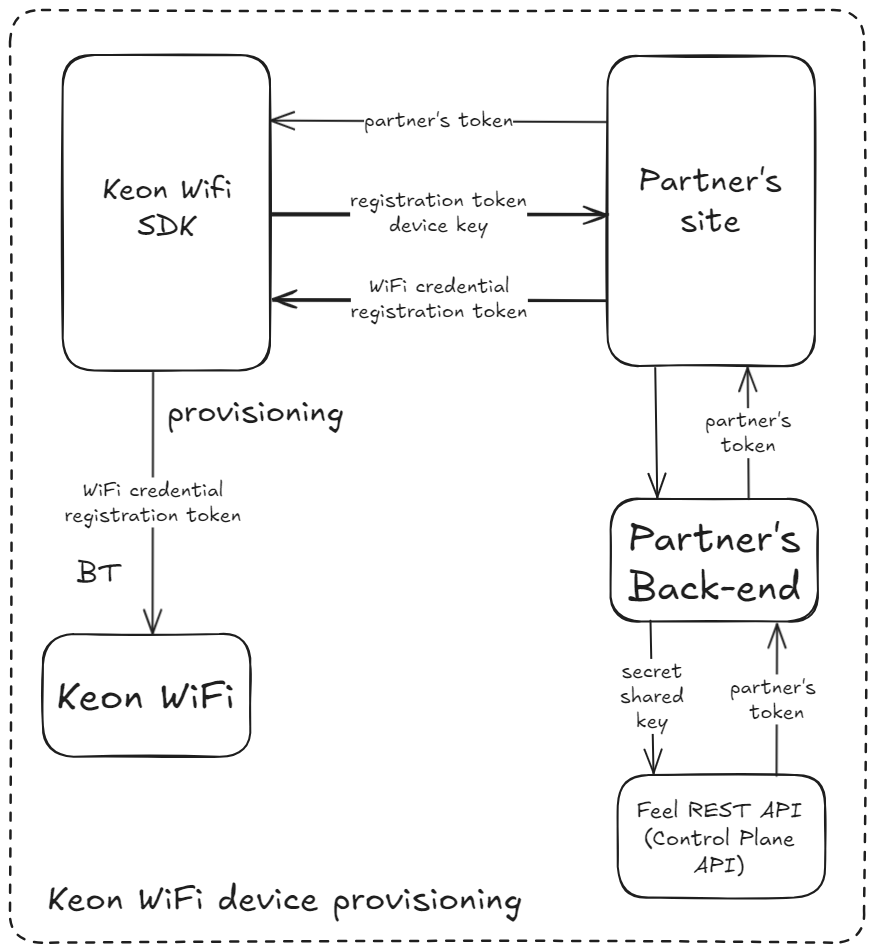
Provisioning sends the customer’s home WiFi network name (SSID) and password, plus a registration token that lists which servers the device should use. When the SDK fetches that token, it also tests network latency and chooses the server closest to the user to keep responses fast.
Provisioning Steps
-
Get a registration token
getTokenForKeonWiFi({ feelAppsToken: "<partner-token>", deviceConnectionKey: string });-
<partner-token>could be obtained from request(fromBefore You Begin):GET /api/v1/partner/<partner-key>/token?user=<user-id> -
device_connection_keyis a unique 8-character string using the following alphabet: 0..9 and A..Z (excluding B, I, O, Q, Z). All characters are uppercase. Generated by the server if not explicitly specified. Used to build a link between the customer and their device.
-
-
Run the provisioning function
provisioningKeonWiFi({ registrationToken: "<registrationToken>", ssid: "<customer’s WiFi name>", password: "<customer’s WiFi password>" });- A popup will list available Bluetooth devices. Select your Keon WiFi device.
Within 3–5 seconds, the SDK sends the network settings to the device, and the device enters WiFi mode.
2. Sending and Receiving Commands & Status Updates
After provisioning, the app and Keon WiFi device communicate over Socket.IO, a real-time messaging protocol.
- Socket.IO Documentation: https://socket.io/
- Client Libraries: https://github.com/socketio
Every command you send (for example, moving the slider) and every status update from the device (like button presses or connection state) goes through this secure, low-delay channel.
For communication with the device - SDK provides the KeonManager class. An instance of this class is returned by the keonWiFiManager function:
// Create a KeonManager instance for ongoing communication
// keonWiFiManager requires feelAppsToken, registrationToken, and a userActionHandler callback
const manager = await keonWiFiManager(
feelAppsToken,
registrationToken,
(message: any) => {
// Handle messages from the device
console.log('Device message:', message);
}
);
KeonManager Class
Connection Management Methods
init()
Function Signature:
async init(): Promise<SocketClient>
Description: Establishes the WebSocket connection to the Feel Technology server infrastructure. Creates a SocketIO client with the configured server URL and access token, registers event handlers for device status updates and user activities, and returns the active socket client instance.
Returns: Promise resolving to the initialized SocketClient instance
close()
Function Signature:
async close(): Promise<void>
Description: Gracefully terminates the WebSocket connection and cleans up resources. Closes the socket client connection and sets the internal client reference to null, ensuring proper cleanup of network resources.
Status and Monitoring Methods
getDeviceStatus()
Function Signature:
getDeviceStatus(): KeonDeviceStatus
interface KeonDeviceStatus {
ble_address: string;
serial_number: string;
battery_status: number;
status_package: string;
encoder_pos: number;
motor_speed: number;
wifi_strength: number;
intensity: number;
stroker_level: number;
firmware_version: string;
status_period: number;
error_code: number;
}
Description: Returns cached status data from the connected Keon device: including battery level, encoder position, motor speed, WiFi strength, intensity settings, firmware version, and error codes.
Returns: Current device status object or null if no status has been received
forceStatusReport()
Function Signature:
async forceStatusReport(): Promise<void>
Description: Sends a command to the server requesting an immediate status update from all connected devices. Triggers the device to send its current status information, which will be received through the status update handler.
Movement Control Methods
moveTo()
Function Signature:
async moveTo(speed: number, position: number)
Description: Commands the device to move to a specific absolute position at the specified speed. Both speed and
position range from 0 to 100.
Parameters:
- speed: Movement speed value
- position: Target absolute position
movementBetween()
Function Signature:
async movementBetween(speed: number, min_position: number, max_position: number)
Description: Initiates continuous movement between two position boundaries at the specified speed. The device will
oscillate between the minimum and maximum positions until a stop command is issued. Both speed and position range
from 0 to 100.
Parameters:
- speed: Movement speed for the oscillation
- min_position: Lower boundary position
- max_position: Upper boundary position
stopCommand()
Function Signature:
async stopCommand()
Description: Stops any ongoing movement operations including single movements or continuous oscillations.
Configuration Methods
setIntensityAdjustment()
Function Signature:
async setIntensityAdjustment(intensity: number)
Description: Configures the device’s intensity settings by sending two sequential commands: speed intensity adjustment and range intensity adjustment. Includes a default 200ms delay between commands to ensure proper processing.
Parameters:
- intensity: Intensity level to set (gets doubled for speed adjustment)
intensity can be:
4= 100%3= 75%2= 50%1= 25%
setIntervalForUpdatingStatus()
Function Signature:
async setIntervalForUpdatingStatus(interval: number)
Description: Configures how frequently the device sends status updates to the server. Adjusts the device’s internal status reporting interval to control the frequency of status messages.
Parameters:
- interval: Status update interval in seconds
Device Management Methods
switchToBtMode()
Function Signature:
async switchToBtMode()
Description: Commands the device to switch from WiFi mode back to Bluetooth mode.
resetCredentials()
Function Signature:
async resetCredentials()
Description: Clears all stored WiFi credentials and connection information from the device. Sends a reprovisioning command that resets the device’s network configuration, requiring it to be provisioned again before WiFi connectivity can be restored.